[ad_1]
What does cannabis, coca leaf, and all coffee have in common? They all contain alkaloids, a powerful group of medicinal compounds found in plants around the world. While little is presently known about cannabis alkaloids, they are suspected to possess impressive medical benefits like other plant alkaloids.
Alkaloids vs. Cannabinoids
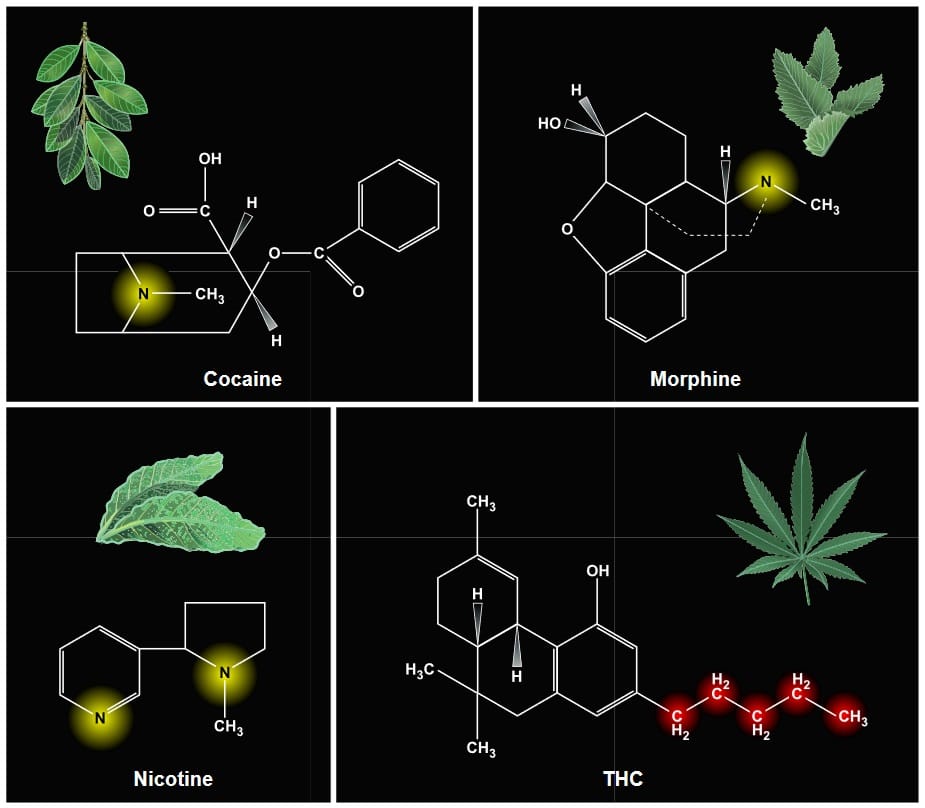
Alkaloids are “one of the most common groups of chemicals that [have] medicinal properties found in plants,” commonly used alkaloids include “morphine, cocaine, nicotine, caffeine, quinine, ephedrine, and many more.” They derive their name, alkaloid, from the word alkali, chemicals that react like bases, counteracting acids. Usually found in the outer tissues of plants, the bitter flavor of alkaloids is believed to be a natural defense in plants to prevent them being eaten by herbivores, similar to cannabinoids and terpenes which both assist in preventing predation.
While cannabinoids like THC, CBD, CBG, and THCv, are oily, lipohpilic (binds to fats), and hydrophobic (do not bind to water) compounds, alkaloids are a very different class of chemicals. The biggest chemical difference between alkaloids and cannabinoids is that all alkaloids include a nitrogen atom which binds to additional hydrogen atoms. Cannabinoids, on the other hand, do not have any nitrogen atoms and contain a chain of carbon atoms, which gives them their oily character.
Despite their differences, efficient methods to extract both alkaloids and cannabinoids from plants is to simply burn the leaves or other parts that contain the chemicals, or perform a chemical extraction. These methods have been used for thousands of years for both types of chemicals; the caffeine in coffee is chemically extracted by brewing with water, cannabis is smoked, and cocaine was originally extracted through chewing or brewed as a tea.
Discovery of Alkaloids in Cannabis
Cannabis is a very complicated plant and “more than 500 compounds have been reported from C. sativa, of which 125 cannabinoids have been isolated and/or identified as cannabinoids.” Non-cannabinoid constituents of cannabis include “42 phenolics, 34 flavonoids, 120 terpenes and 2 alkaloids.” Though, there is some debate over the number of alkaloids which have been identified.
The discovery of alkaloids in cannabis actually manages to predate the discovery of the first cannabinoid, CBN, back in 1896, by more than a decade. In 1881, the first research on the alkaloid cannabinine was presented at the British Pharmaceutical Conference, and two years later another physiologically active alkaloid, tetanocannabin, was discovered. Cannabis alkaloid research then remained dormant until the 1970s.
In 1971, a group of scientists isolated four different alkaloids from cannabis, which they named cannabimines A-D. In 1975, two teams of researchers at the University of Mississippi (UMiss) identified and isolated the first spermidine alkaloid, cannabisativine, from the roots, leaves, and stems of both Mexican and Thai cultivars. The next year, the same researchers at UMiss isolated the second spermidine alkaloid, anhydrocannabisativine and showed that cannabisativine could be converted to anhydrocannabisativine.
While the cannabis alkaloids cannabisativine and annhydrocannabisativine were first discovered in Mexican and Thai cultivars, anhydrocannabisativine has since been “found in plant samples of Cannabis from 15 different geographical locations.”
Which Part of The Plant Has the Most Alkaloids?
Just like how not every part of a cannabis plant has the same amount of cannabinoids, alkaloids are also unequally distributed around the plant. Research has repeatedly shown that, “cannabis roots are not a significant source of cannabinoids or the aforementioned terpenes, but are rich in other compounds, including … alkaloids.” So while terpenes and cannabinoids are concentrated primarily in the trichomes on the leaves, cannabis alkaloids are primarily found in the roots (but can be found in the stems and leaves as well).
Medical Effects of Cannabis Alkaloids
While cannabis alkaloids have a lot of medical potential, the specifics of that potential are unknown. In the case of cannabisativine and anhydrocannabisativine, “no pharmacological information is available,” but it is believed that “there are several compounds in cannabis root with potential anti-inflammatory activity, including alkaloids.”
Other researchers have noted that, as a class of compounds, “alkaloids may be used as analgesics, antibiotics, anticancer drugs, antiarrhythmics, asthma medications, antimalarials, anticholinergics, bronchodilators, laxatives, miotics, oxytocics, vasodilators, psychotropics, and stimulants,” and that likely includes cannabis alkaloids. One study of cannabis alkaloids found them to “have diuretic, analgesic, anticancer, antipyretic, and antiemetic effects.”
In one study, a petroleum ether solution of cannabis alkaloids and cannabinoids had “a course of action comparable to that of atropine,” a drug commonly given to reduce fluid in the respiratory tract during surgery, which “can also treat insecticide or mushroom poisoning.” It is not clear to what extent those observed effects were due to the alkaloids or the cannabinoids.
A Quick Hit
Despite being one of the most common groups of medicinal chemicals found in plants, alkaloids are some of the least known chemicals in cannabis. Early research shows that they may have strong medical benefits as part of the entourage of medicinal compounds in cannabis.
[ad_2]





Leave a Reply